How Tennis Players can Avoid Wrist Injuries

How Tennis Players Can Avoid Wrist Injuries
Tennis is one of the most popular sports in the world. Unlike most sports, tennis is not a contact sport, however, it is a physically demanding exercise. Tennis is often played recreationally by amateurs, and professionally in larger sporting events. As the number of recreational tennis players increases, so does the rate of tennis-related injuries – from 0.05 to 2.9 injuries per player per year or 0.04 to 3.0 injuries per 1000h played.
The most common tennis injuries are tennis elbow, shoulder injuries, stress fractures, muscle strains, knee injuries, wrist strains and fractures, and back injuries. Current epidemiological data suggested that wrist injuries account for higher percentages of total injuries, and frequency fo wrist pain or injury is much higher than previously reported.
What are the causes of wrist injuries in tennis players?
There are several causes of wrist injuries. The wrist is a hinge joint that contains the wrist bones or carpals, joints for metacarpals, and bones of the lower arm: radius and ulna. Also, the wrist is held together by strong dense fibrous connective tissues such as ligaments and tendons. These connect tissues hold the bones of the wrist together and facilitate the smooth movement of the hand.
Blood vessels passing through the wrist ensures adequate blood flow to the distal portion of the hand. Nerves projections from the spinal cord also run through the wrist to innervate muscles of the hand. Damage to any of these structures can result in a wrist injury.
The major cause of wrist injuries in tennis players is prolonged or chronic overuse of the wrist. Biomechanical studies on the serving techniques of tennis players showed that injured players demonstrated kinetics that overload the joints including the wrist.
What are the symptoms of wrist injuries?
Common symptoms of wrist injuries are swelling and tenderness. Most patients complain of pain which increases with wrist mobilization. Other symptoms are bruising, inflammation, and popping sound. Most wrist injuries share common symptoms, and as a result, it is possible for patients to confuse mild and severe wrist injuries. It is very important that patients visit an outpatient center for prompt evaluation of hand.
How to diagnose wrist injuries in tennis players?
Due to the extensive list of wrist injuries possible, there is no simple diagnostic method for evaluating wrist injuries. For a more accurate diagnosis, the physician will obtain a detailed medical history of the patient. A physical examination of the affected hand and surrounding tissues will help the physician to determine the extent of the injury. The physician will massage the soft tissues around the wrist to assess for bone fracture, swelling, and other signs of connective tissue damage.
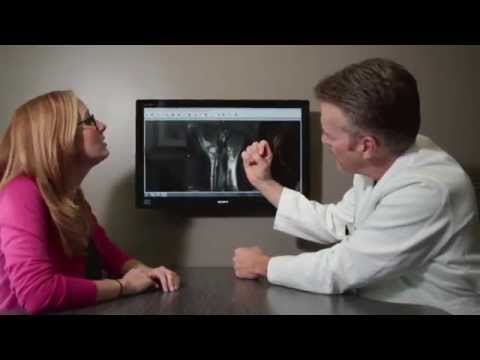
Mild cases of wrist injury can be easily diagnosed and treated. In more severe cases, the physician will recommend medical imaging of the wrist to improve diagnosis. Common imaging tests are x-rays, MRI, CT, and ultrasound combined with arthroscopy. X-ray images are great for visualizing the bones. MRI, CT, and ultrasound scans are used for examining the soft tissues of the wrist. Together, these images can provide an appropriate diagnosis of a wrist injury.
How to treat wrist injuries?
For mild wrist injuries, the athlete or tennis player can do home care remedy. This typically involving resting the injured hand. RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) treatment is often sufficient for benign cases of wrist injuries. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and other over-the-counter (OTC) medications can be used to treat the pain symptoms associated with a wrist injury. Patients are advised to immobilize the hand by wearing a splint or brace
For severe wrist injuries involving a partial or complete tear of wrist ligaments or tendons, and with bone fracture, surgery is usually performed. Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for wrist injuries. It involves making a small cut on the skin and inserting a scope into the tissue to guide the surgical repair of the torn tissues.
Postoperative management of wrist injuries in tennis players?
For non-surgically treated wrist injuries, the patient should wear a hand brace for about 2 weeks. The patient should perform a minimal activity with the injured hand. Following surgery, patients should consult the advice of the surgeon or hand specialist for when to begin hand therapy. Physical therapy and hand exercises should be performed to improve range of motion, enhance blood flow, and to strengthen the muscles of the hand.
How Tennis Players can avoid Wrist Injuries?
Since wrist injuries develop from hand overuse and improper ergonomic methods, recovering patients should take to use proper procedures when playing. How a tennis players grip the racquet can also contribute to the amount of load delivered to the wrist. For example, players who hold the racquet using the Eastern grip have higher chances of radial-sided wrist injuries such as DeQuervain syndrome, Intersection syndrome, and FCR tenosynovitis, while those players with Western and semi-Western grip have higher ulnar-sided wrist injuries like extensor carpi ulnaris injuries.
Athletes and amateur players should perform warm-up exercises before starting a game. Hand and wrist muscles exercises should be encouraged to strengthen the appropriate muscles. Young players should rest between sets to aid muscle recovery. In the case of injuries, players should ensure that the wrist heals properly before resuming play.
Citations
- “Aspetar Sports Medicine Journal – Wrist Injuries in Tennis.” Aspetar – Home, www.aspetar.com/journal/viewarticle.aspx?id=195#.XW1XWChKjIU.
- “Wrist Injuries in Nonprofessional Tennis Players: Relationships with Different Grips – Alberto Stefano Tagliafico, Pietro Ameri, Johan Michaud, Lorenzo E. Derchi, Maria Pia Sormani, Carlo Martinoli, 2009.” SAGE Journals, 6 Mar. 2009, journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0363546508328112?rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&journalCode=ajsb.
- “Common Tennis Injuries Affecting Your Favorite Stars ? Penn Medicine.” University of Pennsylvania Health System | Penn Medicine, www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/musculoskeletal-and-rheumatology/2017/july/common-tennis-injuries-affecting-your-favorite-stars.
- Stuelcken, Max, et al. “Wrist Injuries in Tennis Players: A Narrative Review.” Sports Medicine, vol. 47, no. 5, 2016, pp. 857-868.
The number one thing that causes hand and wrist injuries is an extremely tight grip. This tends to place a player’s wrists in unusual positions that make them more likely to become injured. In order to reduce the risk, athletes should grasp their racquet firmly without squeezing on it.
Certain types of strings can also increase the odds of injury. Polyester strings are stiffer, and therefore cause more vibration to the hands and wrist whenever the ball is hit. Natural gut or nylon strings are somewhat softer, and do not transmit much vibration to the upper extremities. Players can sometimes benefit from changing out their polyester strings, especially when injuries tend to recur frequently in their dominant hand.
Hand and wrist strengthening exercises should be performed as a part of every tennis training program. Many of these exercises can also help increase one’s range of motion, thereby making elbow injuries less likely as well. Conditioning exercises can be performed using light hand weights or resistance bands, and should take no more than five minutes to complete.
Before beginning play, it can be important to stretch the wrist in order to loosen it up somewhat. An effective stretch involves bending the wrist down and flexing the fingers upward. After holding for around 15 seconds, the fingers can then be directed downward in order to stretch the top part of the wrist. Stretches should be performed on both hands for maximum effectiveness. The same stretches should be done as part of a cool down routine as well.
A wrist brace can help provide stability for the joints, thereby preventing tennis injuries. When choosing a brace, make sure it does not have a thumbhole, as this could make serving the ball difficult. Many people find wearing a brace restricts their ability to play whenever they are not used to having it on. For this reason, it is important to wear a brace during practice and informal play before using one during competitive play.
By taking the proper precautions, tennis players can avoid painful injuries to their wrist and hands. Those who do find themselves suffering from such an injury can seek professional help from the Hand and Wrist Institute.