What is the ECU Tendon and What Are Common Problems?
The extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) tendon plays an important role in the movement and stability of the wrist. Located on the ulnar side of the wrist, this tendon is responsible for extension and ulnar deviation. However, as with any intricate part of the body, the ECU tendon is susceptible to a variety of issues that can affect its ability to function properly.
From overuse injuries to traumatic incidents, the ECU tendon can face challenges that cause discomfort, pain, and functional limitations. In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of the ECU tendon — what it is, what factors can cause an issue with it, what common conditions of instability are, and how problems with the tendon can be repaired by the hand surgeons at The Hand and Wrist Institute in Dallas, Texas.
Contents
What Is the ECU Tendon?

The ECU is a tendon located on the ulnar side (the pinky finger side) of the wrist. It’s part of the extensor tendon group in the forearm that’s responsible for extending the wrist and moving the hand toward the little finger, known as ulnar deviation.
The ECU tendon runs down the forearm, crosses the wrist, and attaches to the base of the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand. This tendon plays a key role in ensuring wrist stability and enabling certain movements that involve the hand and forearm, such as lifting things, gripping objects, and bending the wrist. Injuries or conditions affecting the ECU tendon can cause pain, affect mobility, and lead to functional impairments of the wrist and hand.
What Causes Issues With the ECU Tendon?
Various factors can cause issues with the ECU tendon, including:
- Overuse or repetitive strain: Activities involving repetitive wrist movements, especially those requiring forceful or repetitive movement of the wrist toward the little finger, can cause irritation or inflammation of the ECU tendon.
- Trauma or injury: Direct trauma to the wrist, such as falling onto an outstretched hand, can damage or strain the ECU tendon. This can result in tendonitis and can even tear the tendon.
- Wear and tear: Age-related changes and degenerative conditions, such as tendinopathy and arthritis, can affect the ECU tendon’s integrity and function over time.
- Instability: In some cases, the ECU tendon becomes unstable and dislocates from its normal position. This can cause discomfort, a snapping sensation, and difficulty using the wrist.
- Occupational or sports-related movements: Certain occupations or sports requiring repetitive wrist movements that stress the ECU tendon, such as racquet sports, manual labor, and playing certain musical instruments, can increase the risk of ECU tendon issues.
What Are Common Conditions of ECU Instability?
Common wrist conditions related to ECU instability include the following:
- Dislocation: ECU subluxation occurs when the tendon moves out of its normal groove, causing it to shift during certain wrist movements. Dislocation involves complete displacement of the tendon from its normal position.
- Tendon subluxation: This condition occurs when the ECU tendon slips over the bony ulnar styloid. It can cause irritation, pain, and audible snapping or clicking sensations when moving the wrist.
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injuries: ECU instability is associated with TFCC injuries, often due to chronic overuse or a traumatic event. This can cause pain, weakness, and limited wrist function.
- Dorsal capsular intercalated segment instability: This refers to instability in the wrist involving multiple structures, including the ECU tendon, ligaments, and joint capsules. It causes abnormal wrist movement and discomfort.
- Instability-related symptoms: If you’re experiencing ECU instability, you might experience symptoms such as pain along the ulnar side of the wrist, a clicking sensation during wrist movements, weakness, and reduced grip strength.
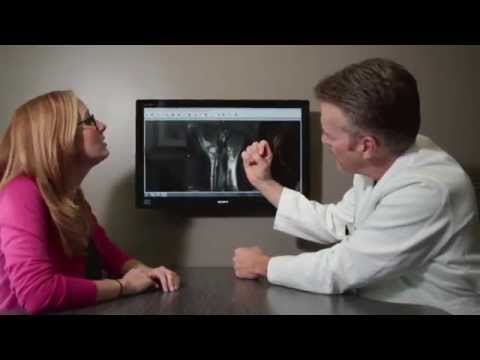
Diagnosing ECU instability typically involves a thorough physical examination; imaging studies, such as MRI and ultrasound; and, sometimes, specific tests to evaluate the integrity and stability of the tendon and its surrounding structures. Treatment approaches range from conservative measures, such as rest, splinting, and physical therapy, to in-clinic or surgical interventions, depending on the severity and underlying cause of your instability.
How Can the ECU Tendon Be Repaired?
Repairing the ECU tendon might involve various surgical procedures based on the nature and severity of your tendon injury or instability. At the Hand and Wrist Institute in Dallas, we may perform the following procedures, depending on your needs:
- Debridement and release: In the case of tendonitis or mild damage, we may remove the damaged tissue or release any tightness around the tendon. This helps reduce irritation and allows for a smoother gliding movement.
- Tendon repair: Surgical repair might be necessary for partial or complete ECU tendon tears. Our Dallas hand and wrist specialists can reattach the torn or damaged tendon to the bone using sutures or other fixation techniques.
- Tendon transfer: In severe cases where the ECU tendon is irreparable, or there’s chronic instability, we might consider a tendon transfer procedure. This involves transferring a different tendon, often the extensor digitorum communis tendon, as a substitute for the ECU if it’s nonfunctional.
- Ligament reconstruction: When ECU instability is associated with ligament damage or TFCC injuries, we can perform surgical reconstruction of the ligaments or TFCC repair, along with ECU tendon management, to restore stability to the wrist joint.
Post-surgery, rehabilitation plays a key role in your recovery. Physical therapy helps restore strength, flexibility, and function in the wrist while allowing the repaired tendon to heal. The specific approach to surgical repair depends on the extent of your injury and our assessment of the most suitable technique for your specific case.
When To Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for ECU concerns if you’re experiencing persistent or severe pain, swelling, deformity, instability, or limited movement in the wrist joint. If your symptoms worsen despite self-care measures, or you suspect an injury or fracture, it’s advisable to seek prompt medical attention. Are you suffering from wrist pain or instability? Contact us today to book an appointment. Our Dallas hand surgeons can provide an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan, getting you on the road to recovery.
person holding hands of another person by Towfiqu barbhuiya is licensed with Unsplash License