Carpal Tunnel vs. Arthritis
To treat hand and wrist pain, you must first know what is causing it. Two common causes of hand pain are carpal tunnel syndrome and arthritis. You may be experiencing one or both of these conditions, causing your hand and wrist to hurt. Don’t let these culprits continue to affect your everyday life.
Contents
- 1 What Is Carpal Tunnel?
- 2 What Are the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- 3 How Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed?
- 4 What Treatments Are Available for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- 5 What Is Arthritis?
- 6 What Are the Symptoms of Arthritis?
- 7 How Is Arthritis Diagnosed?
- 8 What Treatments Are Available for Arthritis?
What Is Carpal Tunnel?
Image via Flickr by wuestenigel
Pressure on the median nerve causes carpal tunnel syndrome, prompting tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand, wrist, and arm. The narrow passageway known as the carpal tunnel is surrounded by ligaments and bones located on the palm side of your hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome tends to affect people who work with their hands doing repetitive tasks such as assembly line work, keyboarding, and carpentry.
Women develop carpal tunnel syndrome at three times the rate of men, possibly because the carpal tunnel area is significantly smaller in women. People who suffer from metabolic disorders or diabetes may also be more prone to developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Also, anyone who has dislocated or fractured their wrist is at a higher risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
What Are the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The first thing you may notice is the sensation that your hand has fallen asleep or is numb at night due to how you hold your hand while sleeping. There may be a tingling or numbness present in your hands that can run up to your shoulder upon waking. Symptoms might flare up during the day, especially if you’re holding something. Specific symptoms include:
- Hand weakness. You may notice that your hand doesn’t have enough strength, especially when holding things.
- Tingling. Carpal tunnel syndrome often causes a tingling sensation in the hand that moves up the arm, sometimes to your shoulder.
- Shocking. You may experience shock-like sensations in your fingers.
- Numbness. The numbness may feel like a tingling, itching, or burning sensation, usually in your thumb and palm or your middle and index fingers.
- Pain. Muscle cramping and pain are common when carpal tunnel syndrome progresses.
- Loss of feeling. You may start to lose feeling in your fingers due to the compression of the median nerve.
How Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed?
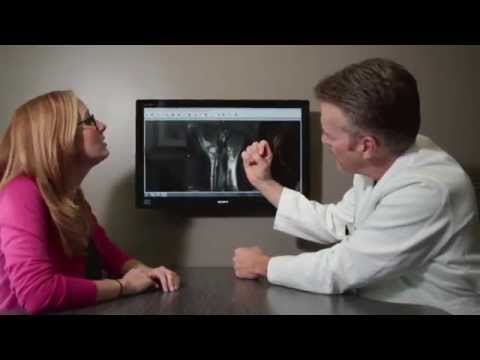
In order to properly diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome, you’ll want to see your health care provider. Your doctor may look for the Tinel’s sign by tapping the palm side of your wrist. They may also have you flex your wrist fully while your arms are extended to test for carpal tunnel syndrome. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or X-rays may be ordered so your doctor can look at your tissues and bones. An electromyogram uses a thin electrode to measure the muscle’s electrical activity. Your doctor may also connect electrodes to your hand, wrist, and arm to measure the nerve signals.
What Treatments Are Available for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
As with many diagnoses, the treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome can vary based on its severity and progression. Treatments may include:
- Exercises. Your health care professional may provide you with exercises designed to stretch and strengthen your hand and wrist muscles. In addition, nerve gliding exercises enable the nerve in your carpal tunnel to move better.
- Immobilization. You may be required to wear a brace or splint to keep your wrist immobilized to relieve the pressure on your nerves. Your doctor may ask that you wear the brace or splint all day or just at night to help rid your hands of that numb or tingling sensation to help you sleep better.
- Lifestyle changes. If repetitive motions cause your symptoms, you’ll want to take more breaks or do particular motions less frequently.
- Medication. Your health care professional may prescribe an anti-inflammatory drug or steroid shots to reduce the swelling.
- Surgery. If none of the other treatments help, your doctor may recommend that you undergo a carpal tunnel release to relieve pressure on your nerve and increase the diameter of the carpal tunnel.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is joint stiffness, swelling, or tenderness of your joints that causes you to experience stiffness and pain It often worsens as you age. Several types of arthritis can be diagnosed, but the most common are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease in which your body’s immune system attacks the synovial membrane which lines and encases the joint. The membrane becomes swollen and inflamed, causing joint pain. Rheumatoid arthritis can eventually destroy bone within the joint and the cartilage.
Osteoarthritis is caused by wear-and-tear damage to the cartilage in your joint. Cartilage is designed to cushion the joint, but with enough damage, you can end up with bone-on-bone grinding. This grinding causes restricted movement and pain. Osteoarthritis affects the entire joint, causing bone changes and deteriorating the connective tissue in the joint, as well as inflammation of the joint lining.
What Are the Symptoms of Arthritis?
Pain in your joints may signify that you have arthritis. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling.
- Stiffness.
- Decrease in range of motion.
- Redness.
Rheumatoid arthritis may also cause a loss of appetite, an overall feeling of tiredness, anemia, and a fever. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint deformity if it’s severe and left untreated.
How Is Arthritis Diagnosed?
If you’re experiencing severe joint pain, you should plan a visit to your health care provider for an examination and treatment options. Your doctor may request blood or joint fluid samples to determine the type of arthritis you have. These tests look for specific antibodies such as rheumatoid factor (RF), antinuclear antibody (ANA), and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP). You also may have imaging scans ordered such as an MRI, CT scan, or X-ray to help rule out bone spurs or other non-arthritis causes.
What Treatments Are Available for Arthritis?
Treatment for arthritis focuses on reducing your pain and preventing further damage. Options include:
- Heat/ice. Using a heating pad of ice pack may alleviate swelling and pain.
- Lifestyle changes. Eating healthfully, losing weight, and exercising regularly may alleviate your symptoms as well.
- Cane/walker. Mobility assistance devices may make it easier to get around.
- Medications. Analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, menthol and capsaicin creams, and immunosuppressants may all help in reducing your inflammation.
- Physical therapy. Exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint may be to your benefit.
- Surgery. Joint replacement and joint fusion are two surgical options for arthritis treatment.
If you or someone you love is experiencing pain in the hand or wrist, reach out to The Hand and Wrist Institute. We have the specialized knowledge and experience necessary to diagnose and treat any issues surrounding the hand or wrist.