Can a Ganglion Cyst Become Cancerous?
Ganglion cysts are one of the most common types of hand cysts, accounting for 60% to 70% of soft-tissue masses found in the hand and wrist. While these fluid-filled lumps are harmless, their appearance can cause you to wonder if ganglion cysts are dangerous. Our Dallas-Fort Worth team put together this comprehensive guide to address that concern and inform you how we can help with diagnosing and managing ganglion cysts.
Contents
- 1 What Are Ganglion Cysts?
- 2 Causes Behind the Formation of Ganglion Cysts
- 3 When Should You Be Concerned?
- 4 The Process of Development: How Do Ganglion Cysts Evolve?
- 5 Standard Procedures for Diagnosing Ganglion Cysts
- 6 Treatment Options and Future Management
- 7 Living With a Ganglion Cyst: Real-Life Considerations and Support
- 8 Are You Concerned About a Growth You Have?
What Are Ganglion Cysts?
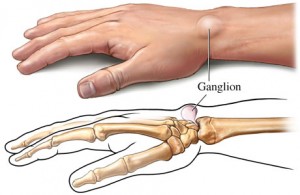
Ganglion cysts are benign lumps that typically form along tendons or joints, particularly in your wrists, hands, and feet. While ganglion cysts aren’t cancerous, they can sometimes be mistaken for other types of growths, like mucoid cysts, carpal boss, and synovial cysts. When comparing a ganglion cyst vs. cancer, there are notable differences. While cancerous tumors are firm and less pliable, ganglion cysts are filled with a soft, jelly-like fluid and are softer and moveable. They’re most commonly found in women aged 20 to 50. Statistically, women are three times more likely to develop this condition than men.
Causes Behind the Formation of Ganglion Cysts
The exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unknown. They’re believed to develop due to joint stress or irritation that causes a cyst to form. Risk factors include repetitive motion, previous joint or tendon injury, and underlying joint conditions such as arthritis.
When Should You Be Concerned?
Ganglion cysts may present the following signs or symptoms:
- Visible lump that varies in size
- Painful joint, especially if pressing on a nerve
- Limited joint mobility in the affected area
If a lump changes rapidly in size, becomes firm, or is immobile, consult your health care professional immediately.
The Process of Development: How Do Ganglion Cysts Evolve?
Ganglion cysts develop when synovial fluid, which lubricates joints and tendons, escapes into the surrounding tissue. This fluid builds up, forming a sac-like structure that may start small and grow over time. The size of a ganglion cyst can vary, often increasing with activity that stresses the joint or tendon and decreasing during rest periods.
While they can grow larger and become more noticeable, some ganglion cysts may go away on their own. However, the exact factors influencing their growth and recurrence remain uncertain, making it important to monitor any changes and consult your health care provider if needed.
Standard Procedures for Diagnosing Ganglion Cysts
Our health care providers diagnose ganglion cysts through a physical examination. The doctor assesses the lump’s texture and mobility. We may order an ultrasound or MRI to confirm the presence of fluid and rule out other conditions. We may also aspirate (extract fluid) from the cyst to analyze its contents.
Addressing the Big Question: Can a Ganglion Cyst Become Cancerous?
Because ganglion cysts are benign by nature, they can’t become cancerous and pose no risk of developing into malignant tumors. Misdiagnosis is rare when proper diagnostic steps are taken.
Treatment Options and Future Management
Treatment for ganglion cysts may involve conservative or surgical treatments.
Nonsurgical Treatments
Observation is often sufficient for small, asymptomatic cysts, as many resolve independently. Other options include immobilization to reduce stress on the joint and aspiration to drain the fluid, though cysts may recur.
Surgical Treatments
Ganglion cyst hand surgery is recommended for persistent, painful, or recurrent cysts. During surgery, the entire cyst, including its stalk, is removed, helping to minimize recurrence by an estimated 15% to 20%.
Living With a Ganglion Cyst: Real-Life Considerations and Support
Living with a ganglion cyst can vary depending on its size, location, and impact on daily activities. These cysts are asymptomatic and require no treatment, allowing them to go unnoticed or managed without medical intervention. However, if a cyst becomes painful or interferes with mobility — such as gripping objects or performing repetitive tasks — it may impact your quality of life.
Simple modifications such as using ergonomic tools, wearing a brace, or avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms can help. Emotional support and education play a significant role for those living with a ganglion cyst. While the condition isn’t life-threatening, uncertainty about its recurrence or changes in size can lead to anxiety. Connecting with your health care provider or a support group can provide reassurance and guidance.
Preventing Recurrence: Can You Prevent a Ganglion Cyst?
Unfortunately, there’s no guaranteed way to prevent a ganglion cyst from forming or recurring after treatment. These cysts are believed to develop as a result of joint irritation or trauma, though the exact cause is often unclear. While minimizing repetitive stress or trauma to the joints may reduce risk, it’s not a foolproof prevention strategy.
If you’re prone to ganglion cysts, maintaining joint health can help. Prevention might include strengthening exercises, proper joint alignment, and avoiding overuse of affected areas when possible. Monitoring the cyst for early signs of growth or discomfort and consulting a specialist can also help reduce recurrence.
Outlook/Prognosis: Understanding the Long-Term Perspective
The long-term outlook for those with a ganglion cyst is overwhelmingly positive. These cysts are benign and not a cause for serious health concerns. Many resolve independently without treatment, while others can be effectively managed through nonsurgical or surgical methods. For anyone who undergoes surgical excision, the recurrence rate is relatively low, typically between 15% and 20%. While ganglion cysts can interfere with daily activities, their noncancerous nature provides reassurance. Proper care and monitoring allow you to lead a normal, active life without considerable limitations.
Empowering Patients: Questions To Ask Your Health Care Provider
Knowledge is the key to managing a ganglion cyst confidently. Consider asking your health care provider these questions:
- What caused my ganglion cyst, and could it come back after treatment?
- Are nonsurgical treatments appropriate for my situation, or should I consider surgery?
- What are the risks and benefits of surgical removal?
- How can I minimize discomfort and prevent recurrence?
- Could my cyst be mistaken for another condition?
Being proactive in your care allows you to make informed decisions and work collaboratively with your health care provider to achieve the best outcomes.
Are You Concerned About a Growth You Have?
Ganglion cysts aren’t cancerous, though their appearance may be troubling. Proper diagnosis and management are essential to alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. If you’re in Dallas-Fort Worth or the surrounding area and are experiencing discomfort or uncertainty, seeking medical advice from our specialists at The Hand and Wrist Institute can provide clarity and peace of mind. For expert care and solutions tailored to your needs, schedule a consultation today.