Biceps Tendinitis
What is Distal Biceps Tendonitis?
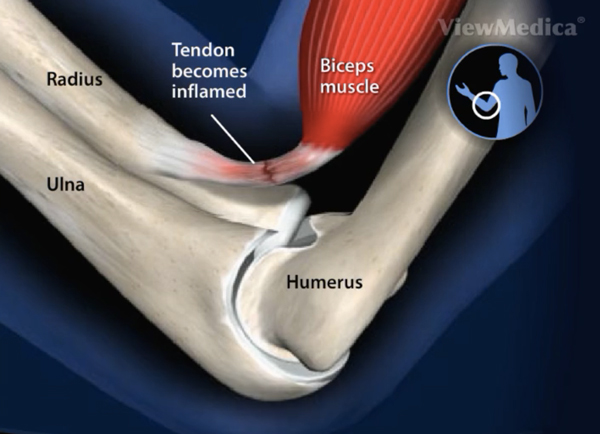
The biceps brachii muscle is located at the front of the upper arm. Its function is to allow flexion at the elbow and supination (rotation) of the arm. Tendons are tough rope-like connective tissues that attach muscle to bone to allow movement. The long head of the biceps tendon attaches to the glenoid socket at the top of the shoulder while the short head articulates with the coracoid process on the shoulder blade. The distal biceps tendon attaches the lower aspect of the muscle to the radial tuberosity in the joint. Distal biceps tendonitis describes irritation or inflammation of the distal biceps tendons causing soreness and pain in the front of the elbow.
What causes Biceps Tendonitis?
Distal biceps tendonitis is often caused by injury, overuse, or repetitive movement of the arm, particularly repetitive wrist rotation or elbow bending movements. Athletes such as gymnasts, swimmers and weightlifters are therefore at higher risk for developing this condition. Intense activity that pulls a bent elbow straight or involves strenuous supination can cause a strain to the tendon. Biceps tendonitis can also occur as a result of other elbow conditions such as arthritis.
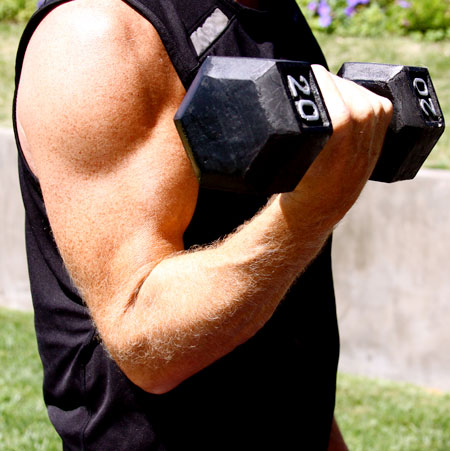

What are the symptoms of Distal Biceps Tendonitis?
Initially, the tendon will become red and swollen with pain or soreness being the primary complaint. The pain is usually located in the front crease of the elbow known as the antecubital fossa. Tenderness worsens with activity and snapping sensation or sound may happen occasionally. Over time the tendon’s outer covering (sheath) will thicken as will the tendon itself. In later stages, inflammation may cause the tendon to start to unravel.
How is Distal Biceps Tendonitis diagnosed?
A detailed history is important for proper diagnosis. The patient’s age, occupation, hobbies, and pertinent comorbidities are all considered. A physical will exam the site, range of motion, and nature of the pain. The physician may also perform special physical examination tests to confirm diagnosis. X-rays are used to visualize any problems in the joints while MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and ultrasound can show damage to soft tissues like the tendon.
How is Distal Biceps Tendonitis treated?
Non-surgical
Most clients respond well to non-surgical intervention. The first line of treatment includes resting the extremity and taking over the counter medications such as ibuprofen or aspirin to manage the pain and inflammation. Ice can be applied for 10 to 15 minutes four times a day during the initial two days of treatment. Physical therapy or gentle stretching may be recommended. In chronic, more severe cases steroid injection may prove beneficial for relief of symptoms. The physician will determine the best course of therapy based on individual needs.
Surgical
Rarely surgery may be indicated in cases with no or minimal improvement using the non-surgical modalities. These procedures can be performed thru which a small incision. If present, degenerative tissues can be debrided and the tendon is restored. Alternately the surgeon may repair the tendon in the case of partial rupture or other damage.
Post-surgical rehabilitation is dependent on the procedure performed. Although the arm may require a sling for a few weeks some basic activities (eating, writing, and washing) can be resumed even sooner. Some activities will be restricted to allow the tendon to heal properly. The doctor will order physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility to the arm. Most patients will regain full range of motion without pain.
Why See Dr. Knight for Biceps Tendinitis?
As always, it is prudent to select a physician or surgeon who is recognized as an experienced specialist. Dr. John T. Knight is a renowned Orthopedic Surgeon who has spoken and appeared on Good Morning America, CNN and radio. Dr. Knight’s background and experience has also been featured in major publications. Educated at Louisiana State University School of Medicine, and studying and completing a Hand and Upper Extremity Fellowship from Joseph H. Boyes, Dr. Knight began his career more than twenty years ago.
He is acknowledged as a prominent hand and wrist surgeon who specializes in innovative treatments that include minimally invasive techniques for the hand, wrist, and upper extremities. With twenty years of experience and 15,000 medical procedures to his credit, Dr. Knight offers the top credentials that all patients deserve.
Dr. Knight is excited to be serving residents throughout the Dallas area. He’s one of the best hand doctors in Dallas and if anyone can help, he can. Come to our Dallas office or Southlake hand and wrist center at your convenience.
(817) 382-6789
Disclaimer
HandAndWristInstitute.com does not offer medical advice. The information presented here is offered for informational purposes only. Read Disclaimer