Animal Bites
Contents
What is an Animal Bite?
Any animal that has teeth can bite, whether domesticated or wild. In the United States, dogs and cats cause the vast majority of animal bites. Exotic animals kept as pets such as snakes, monkeys, and domesticated ferrets account for a small percentage of animal bites. Aside from tissue damage, one of the main concerns when an animal bites a human is the risk of infection. Rabies is associated with bites from bats, foxes, skunks, and raccoons, but must also be considered in bites from cats or dogs with unknown vaccination status. Numerous other organisms found in the mouths and saliva of animals also cause infections. Infection of an animal bite may result in localized cellulitis or an abscess, but can also spread to other parts of the body through the circulatory system causing sepsis, a serious and potentially fatal complication. For this reason, all animal bites, no matter how minor they appear, should be evaluated by a medical provider.
Animal bites which occur on the hand are especially prone to infection. The blood supply in the extremities is relatively poor compared to the blood supply in the trunk of the body. Also, bones, ligaments, and tendons are located just below the surface of the skin and are easily exposed to infection in a bite injury.
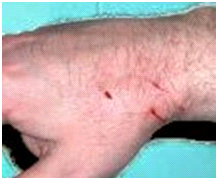
What are the symptoms of an Animal Bite?
Crush injuries of the hand caused by an animal bite may or may not break the skin and may fracture the small delicate bones of the hand. Pain, bruising and swelling, and decreased range of motion may occur depending on the extent of the crush injury. Puncture wounds break the skin. These types of wounds are especially dangerous because they introduce organisms deep into the tissues of the hand. Occasionally, the tip of the animal’s long tooth will chip off and remain hidden in the wound acting as a nidus for infection. Animals with very strong jaws may tear flesh away from the bones of the hand, causing significant damage and disfigurement.
How is an Animal Bite diagnosed?
An animal bite of the hand is usually diagnosed by the history furnished by the victim. It is essential to note which species of animal caused the bite and, if domesticated, whether the animal has been vaccinated for rabies. Imaging studies may be needed to look for foreign bodies and determine the extent of bone, ligament, tendon, nerve, or vascular damage present.
How is an Animal Bite treated?
Non-surgical
Animal bites on the hand should be washed as soon as possible with soap and water and bandaged before seeking emergent care. In the emergency department, the wound will be anesthetized, irrigated, and inspected for foreign bodies. Debridement may be indicated to remove damaged tissue which could impede healing. Most often, the wound will not receive sutures but will be allowed to close on its own. A tetanus shot will be given if the patient has not received one in the past year. Antibiotics will be prescribed based on the species of animal which inflicted the bite, and rabies treatment will be initiated if indicated.
Surgical
Surgery will be required if severe injuries are present. An open fracture will need surgical repair, as will any damaged tendons or ligaments resulting from the bite. The type of bone fractured will dictate the type of treatment required and may include the use of casts, splints, and surgery.
How can Dr. Knight help you with Animal Bites?
Being bitten by an animal can be a traumatic experience, and it is in your best interest as a patient to seek care from a doctor who is both compassionate and competent. As a hand surgeon, Dr. Knight possesses a breadth of knowledge of treatment for a variety of hand injuries, including animal bites. You will be in good hands with Dr. Knight. To learn more about general conditions such as animal bites, click here to continue reading.
Dr. Knight is one of the premier hand surgeons in Dallas. We invite you to visit him at our Southlake office or Dallas office today.
Animated Videos
Disclaimer
HandAndWristInstitute.com does not offer medical advice. The information presented here is offered for informational purposes only. Read Disclaimer